Gastrointestinal Problems
Knowledge is Power.
True/False - Quiz: Do You Understand Gastrointestinal Problems?
Information - Gastrointestinal Problems
 Gastrointestinal (GI) issues are very common, and many of them have similar symptoms. Gastrointestinal symptoms can cause a great deal of discomfort, and some may be related to more serious health issues.
Gastrointestinal (GI) issues are very common, and many of them have similar symptoms. Gastrointestinal symptoms can cause a great deal of discomfort, and some may be related to more serious health issues.
Types of Gastrointestinal Problems
Here are some of the most common gastrointestinal symptoms, but remember, it’s important to see your physician for diagnosis and treatment.
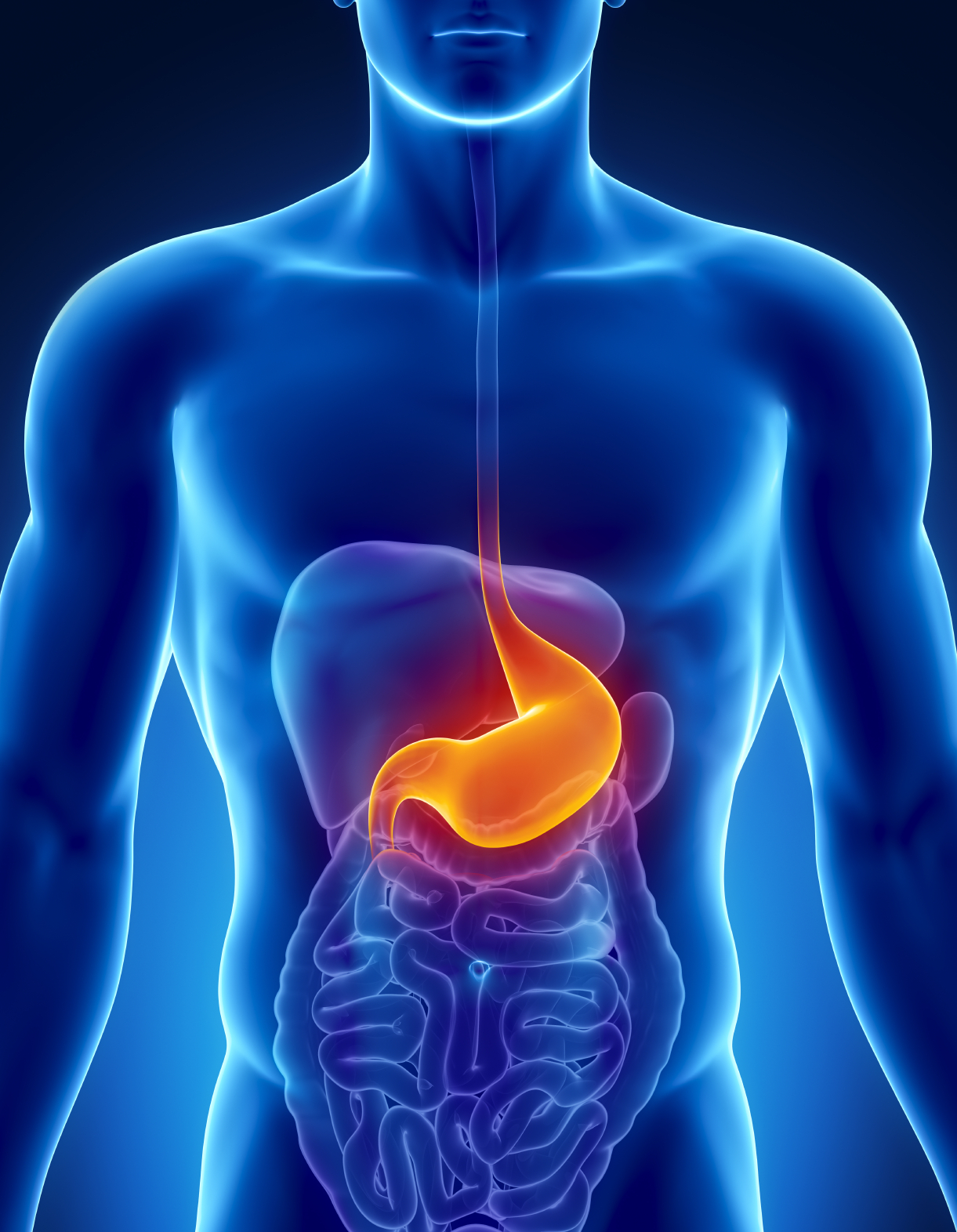 • Abdominal pain: There can be many causes of stomach pain, including digestive problems, appendicitis (ruptured appendix), kidney infection, food poisoning, stomach flu (viral gastroenteritis), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and parasitic infections.
• Abdominal pain: There can be many causes of stomach pain, including digestive problems, appendicitis (ruptured appendix), kidney infection, food poisoning, stomach flu (viral gastroenteritis), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and parasitic infections.
• Blood in the vomit or stool: Gastrointestinal bleeding can be related to health issues such as ulcers, cancers, hemorrhoids or anal fissures and diverticulitis.
• Constipation: Often caused by poor diet and an inactive lifestyle. Other constipation causes include medications, IBS, pregnancy, lupus and Parkinson’s disease.
• Diarrhea: People may get diarrhea related to food poisoning, stomach flu, lactose intolerance, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome and celiac disease.
• Heartburn: This is a symptom of GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), caused by acid refluxing back into the esophagus. It often occurs after meals or at night.
• Nausea and vomiting: There are numerous reasons you might feel nauseated or vomit, including pregnancy, intense pain, medications, food poisoning, viral gastroenteritis, heart attack or ulcer.
Treatment of Gastrointestinal Problems
Because there are so many different types of gastrointestinal problems, there is no on treatment. The first step in treating gastrointestinal problems is to identify any underlying condition or medication that may be causing symptoms. To treat symptoms of constipation, you can drink plenty of fluids, eat more fibre and perhaps use a laxative in the short-term. To treat diarrhea or nausea and vomiting, you can drink more fluids.
However, in the long-term it's important to identify causes, triggers and symptoms of your gastrointestinal problem to effectively treat it. If you experience gastrointestinal symptoms, your physician may refer you to a gastroenterologist, a physician who is specially trained to diagnose and treat diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and liver.
Talk to your family physician if you'd like more information on gastrointestinal problems.
Visit HealthChoicesFirst.com for more videos and resources on family health.
Print this Action Plan and check off items that you want to discuss with your healthcare provider
-
Stomach pain can be caused by digestive problems, appendicitis (ruptured appendix), kidney infection, food poisoning, stomach flu (viral gastroenteritis), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and parasitic infections.
-
Gastrointestinal bleeding can be related to health issues such as ulcers, cancers, hemorrhoids or anal fissures and diverticulitis.
-
Constipation can be caused by poor diet, an inactive lifestyle, medications, IBS, pregnancy, lupus and Parkinson’s disease. People may get diarrhea related to food poisoning, stomach flu, lactose intolerance, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome and celiac disease.
-
Heartburn is a symptom of GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), caused by acid refluxing back into the esophagus. It often occurs after meals or at night.
-
Because there are so many different types of gastrointestinal problems, there is no on treatment. The first step in treating gastrointestinal problems is to identify any underlying condition or medication that may be causing symptoms.