Nutrition and COPD
Knowledge is Power.
True/False - Quiz: Do You Understand Nutrition and COPD?
Information - Nutrition and COPD
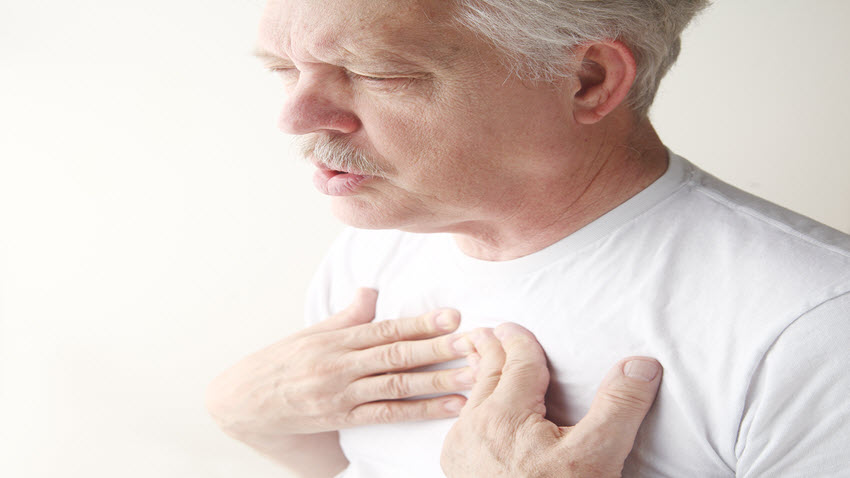 If you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), meal planning can help you live better and feel better. By eating a healthy diet for COPD, you can ensure you’re getting enough nutrients, and reduce or prevent symptoms and side effects.
If you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), meal planning can help you live better and feel better. By eating a healthy diet for COPD, you can ensure you’re getting enough nutrients, and reduce or prevent symptoms and side effects.
What Should People with COPD Focus on Eating?
1. Fiber
Fiber is an important part of everyone’s diet, and is especially beneficial for those with COPD. Fiber helps move food through your digestive system, and it can help control cholesterol and blood sugar levels. Look for high-fiber foods such as:
- Fruits (apples, oranges, strawberries)
- Vegetables (yams, sweet potatoes, broccoli)
- Whole grains (whole grain bread & pasta, oats, brown rice, spelt, buckwheat)
2. Protein
Protein is an essential component for overall health and it can even help fight off infections. Good sources of protein include:
- Lean meats
- Poultry
- Fish
- Eggs
- Beans
- Nuts
- Peanut and nut butters
- Tofu
3. Phosporus
Up to half of COPD patients have low phosphorus levels due to poor nutrition and/or certain medications. Phosphorus contributes to healthy lung function, so look to include foods such as:
- Dairy products
- Meat
- Fish
- Eggs
- Nuts
- Beans
4. Magnesium
Magnesium is another mineral that contributes to healthy lung function. Foods high in magnesium include:
- Dark green vegetables
- Tofu
- Whole grains
- Beans and lentils
5. Calcium & vitamin D
Patients with COPD need to eat foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to keep bones healthy and strong. One side effect of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is weak and brittle bones. Include food such as:
- dairy products
- canned fish such as sardines & salmon (with the bones!)
- almonds
- collard greens & broccoli
- fortified orange juice
6. Sodium
Excess dietary sodium can cause fluid retention which makes breathing difficult.
- Choose more fresh, unprocessed foods
- Use less packaged, prepared foods
- Read food labels for sodium values
- Use more herbs, spices and salt-free seasonings to add flavour
COPD Complications and Nutrition
1. Breathlessness
Some patients experience breathlessness during or after a meal which can effect the ability to eat. You can reduce or prevent this symptom by:
- Taking small bites
- Chewing slowly
- Eating smaller meals
- Drinking liquids after a meal, not during
- Clearing mucus from the airways before eating
 2. Weight Control
2. Weight Control
Patients with COPD may be under or overweight depending on the individual. If you have chronic pulmonary obstructive disease and are underweight, you may need to add nutritional shakes or high-calorie foods to your diet. If you’re overweight or obese, you may need to go on a low-calorie diet. Ask your healthcare provider about the right options for you.
3. Water Retention
Water retention can cause uncomfortable symptoms for people with COPD. Always check labels for the sodium content, and avoid adding salt to your food. If you want to add flavour, use herbs or salt substitutes.
4. Medications
COPD medications can interact with certain foods, especially caffeine and alcohol. Talk to your healthcare provider about your medications and possible interactions.
Talk to your healthcare provider if you'd like more information on nutrition and COPD.
Visit HealthChoicesFirst.com for more videos and resources on family health.
Print this Action Plan and check off items that you want to discuss with your healthcare provider
-
Increase daily intake of dietary fiber.
-
Ensure the protein content of the diet is meeting nutritional requirements.
-
Assess dietary vitamin and mineral intake to ensure micronutrient needs are met.
-
Determine healthy weight range and create a plan to reach goal weight.
-
Speak with a healthcare professional regarding possible interactions between the diet and COPD medications.